Describe Three Types of Differentiated Cells
Types of epidermal cells. Blood circulates through the arteries and veins with each of the blood cell types red blood cells white blood cells and platelets carrying out different functions throughout the body.

Cell Differentiation Tissue Learn Science At Scitable
Epithelial cells have a sheetlike structure that protect underlying cells.

. TCR BCR and cytokine signals. In addition some cells divide continuously throughout life to replace cells that have a high rate of turnover in adult animals. There are only about 200-800 monocytes per mm 3 of blood.
The T - cell effector functions of CD4 - Th cells is to secrete the cytokines the effector functions of Tfh cells is to protect the immunity by helping the B cell create antibodies that fight against foreign pathogens. When a cell differentiates becomes more specialized it may undertake major changes in its size shape metabolic activity and overall function. Amniotic fluid-derived cell line.
Dendritic cell - A type of antigen presenting cell that processes pathogens and foreign proteins. Both the compact and spongy bone tissues are composed of 3 main types of bone cells. The multipotent hematopoietic stem cells give rise to many different cell types including the cells of the immune system and red blood cells.
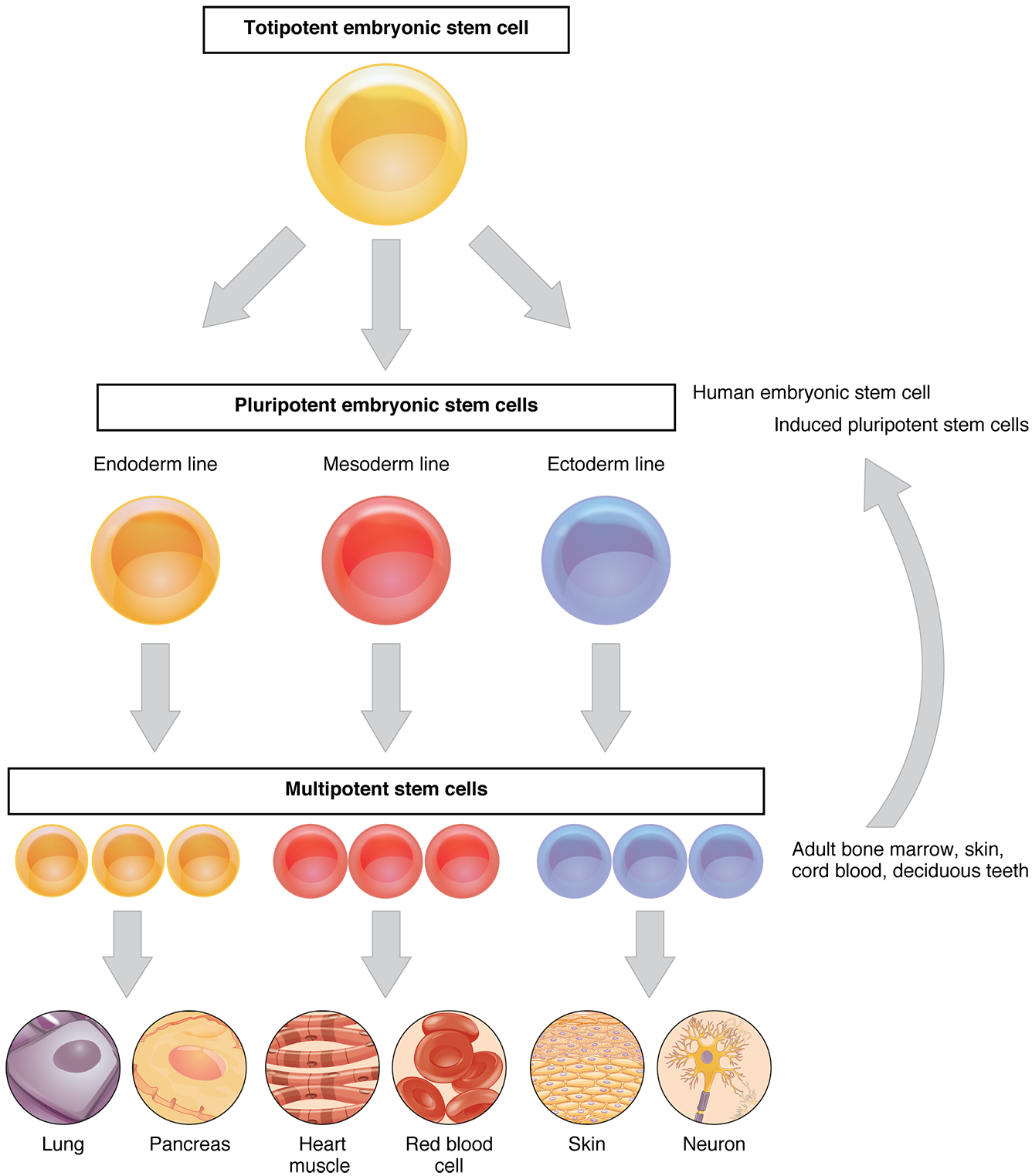
If a cell only receives one of the signals TCR or BCR the cell will become useless. Cell differentiation emanates from stem cells which are cells capable of differentiation. A few types of differentiated cells never divide again but most cells are able to resume proliferation as required to replace cells that have been lost as a result of injury or cell death.
Fibroblasts mast cells and macrophages. 1 Stem cell divides to yield another stem cell and a partially differentiated progenitor cell. These cells are processed in the thymus gland under the influence of the hormone thymosin.
Monocytes are the largest of the types of white blood cells. T lymphocytes are another type of lymphocyte differentiated in the thymus and important in cell-mediated immunity. This vital fluid performs the critical functions of.
Allows cells to send signals and provide instructions to other cells. There are three types of epidermal cells that play the primary role of protecting the plant from environmental factors such as high temperatures pathogens chemical exposures eg. When a group of individualized muscle cells that are bundled together shorten or contract in a coordinated fashion movement is produced.
Structure and Functions of Epidermal Cells Pavement cells. If a cell receives all three signals it will mature into an effector cell. Types of Cells in the Human Body.
Nerve cells are long extensions enabled to conduct electrical impulses from one body part to another. Skeletal muscle composed of thousands of muscle cells attaches to bones and powers movement. List and describe the three different tissue types found in plants.
All cells in an organism contain the same type and sequence of DNA however. The epidermis contains many types of cells including keratinocytes melanocytes Langerhans cells and Merkel cells. These bone cells are embedded in the matrix of bony tissue and perform many vital functions.
It consists of three major types of cells. They are differentiated into three sub-cells as. These bone cells are Osteoclasts Osteoblasts and Osteocytes.
Describe three types of differentiated cells. There are many different types of cells in the epidermis top layer of the skin. Cell differentiation produces different types of cell in animals due to the expression of different genes.
Cytotoxic T cell - Adaptive CD8 immune cell that kill infected cells when activated. There are three types of signals. Give an example of where in the plant you would find each cell type.
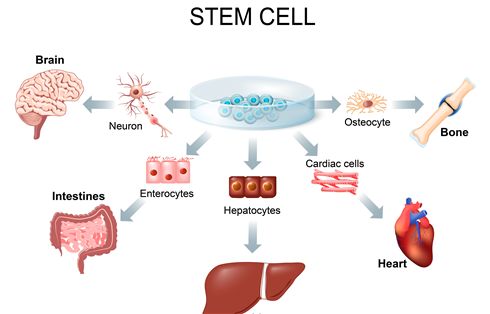
Skeletal muscle smooth muscle and cardiac muscle 2. Cell Types - Human. Epithelial cells skin fibroblasts endothelial cells lining the blood vessels and smooth muscle cells liver cells nerve cells and human cardiac muscle cells are examples of differentiated cells.
CD8- cytotoxic cells cause destruction of particle cells by producing more FasL at the surface and binding together Fasof the target cell. Muscle cells are the building blocks of three types of muscle. Normally 7-8 of human body weight is from blood.
These bone cells have distinct features structure and considered essential functions. List and describe the three different cell types found in some plants. Endothelial cells are the cells that form the lining of blood vessels and are connected to one another via intercellular junctions.
C Natural killer cells. Fibroblasts and mast cells are called - fixed cells because they are residents in a specific tissue for a for a certain period of time unlike wandering cells macrophages which in case of infection or injuries appear in the tissue. 3 Cell with more restricted fates are pluripotent.
Endothelial cells are highly adaptable. Monocytes are agranulocytes meaning they have few granules in the cytoplasm when seen under the. In adults this totals up to 45-6 quarts of blood.
B B lymphocytes and. Cell differentiation is the process whereby cell types with specific functions are produced. Cell Types - Animals.
-Describe the 3 different types of lung carcinomas Squamous-cell carcinoma most common Begins with transformation of bronchial epithelium into stratified squamous from ciliated pseudostratified epithelium Dividing cells invade bronchial wall cause bleeding lesions Dense swirls of keratin replace functional respiratory tissue Adenocarcinoma Originates in mucous. Types of Bone Cells. The shape of different immune cells in the body.
3 Types of Blood Cells and Their Functions. 2 Cells that give rise to any differentiated cell type are totipotent. Depending on the APC a naïve cell comes across it can become an effector T cell.
The lymphocytes are the master cells of the immune system. 4 Stem cells may be present in adult organs or migrate from the bone marrow to replace damages cells.
Difference Between Stem Cells And Differentiated Cells Definition Morphology Types Function Examples
No comments for "Describe Three Types of Differentiated Cells"
Post a Comment